Chris's camera pages
Some possible causes of shutter-cocking rack failure on the Retina IIIc and similar models.
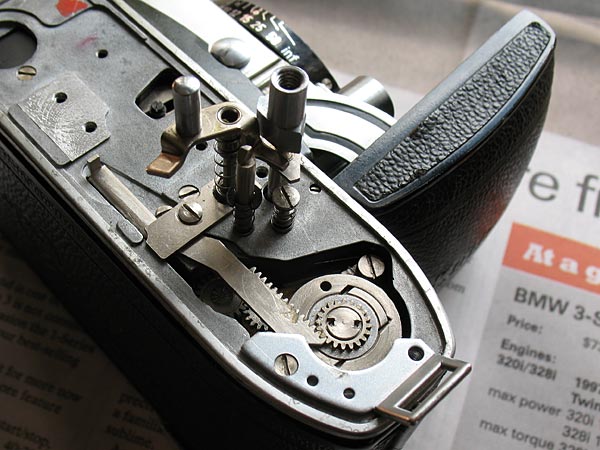

The shutter-cocking rack in the Retina IIIc and similar models is an essential connection between the film advance and the shutter. This is one of a number of items in the chain of components linking the two, so that when the film is advanced, the shutter is simultaneously cocked. It is probably also the component most prone to failure on these models.
It is worth noting that the earlier Retina Ia & IIa models also used a shutter-cocking rack, but it was a different design, thicker in cross-section, stiffer, better supported, and was not prone to failure. Those models had different weaknesses.
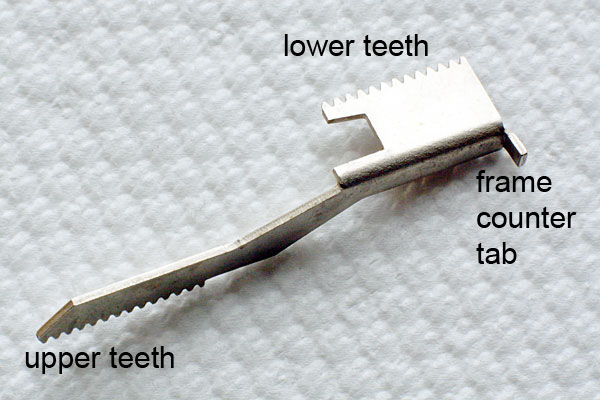
The following faults are those that may be found in an otherwise correctly assembled camera, typically one that has been working apparently normally prior to rack failure.
This is not meant to be an exhaustive list, a camera with no known history may well have been incorrectly assembled before you received it, and so any number of serious problems may have been introduced at that time, most notably, incorrect timing of the gearing resulting in some component hitting a hard stop. Of course, on a camera that has seen a great deal of use, the cocking rack may just be worn-out.
Causes of upper rack tooth damage
Starting from the end closest to the film advance shaft, things that can cause excessive wear and stripping of the teeth on the rack are as follows.
- Condition of the gear on the top of advance shaft, teeth should be all present and show no deformation.
- The screws holding down film advance bushing may be loose, especially the shoulder screw.
- Worn bushing.
- Loose screws holding the film advance shaft plate at the bottom of the camera.
- Friction from damage to, or dust and grit build-up under, the right-hand strap-lug bracket.
- Friction from dust and grit build-up under clamp plate.
- Friction from damage to, or dust and grit build-up in frame counter mechanism in top cover.
- Incorrectly adjusted frame counter.
- Friction from incorrectly positioned shaft assembly bracket, or dust and grit build-up at that point.
- In addition, all the possible faults listed for lower rack teeth damage below.

Causes of lower rack tooth damage
- Excessive end float of shaft assembly relative to rack caused by an incorrectly positioned shaft assembly bracket.
- Dust or grit build-up at gear and cover at front end of shaft assembly
- Excessive friction from gummy lubricants, or dust and grit build-up between curved rack, curved guide and the outer shutter case known as the ring assembly.
- Excessive friction caused by distortion to the ring assembly from drop damage or incorrect reassembly.
- Any excessive load caused by problems inside the shutter itself.

Causes of excessive load from faults in the shutter
- The cocking ring assembly may not move freely due to drop damage, gummy lubricant, or dust and grit build-up. This may occur on the top outer surface where it contacts the shutter speed cam, where the tab on the edge of the cocking ring runs over the edge of the shutter case, or on the inside diameter where it revolves around the central tube on the mechanism plate assembly.
- Dust or grit build-up on the teeth of the gear assembly.
- The cam on the main drive assembly that contacts the retard gear train may not be lubricated and as a result fails to slide over the metal surface smoothly.
An 'external' cause of shutter-cocking rack problems
One possible factor well worth noting, since it is so easy to avoid trouble, is that the design of the camera allows the film to be advanced, and so the shutter to be cocked, with the front cover either in the normal open-ready-for-shooting position, or with the front cover closed.Some Retinas allow winding with the camera front closed without any problems at all, but on others there is a distinct stiffness, sometimes very marked. To avoid any such problems you are best advised to simply never use the film advance lever with the front of the camera closed.The root cause of the alignment problem does not lie with the components of the cocking mechanism as you might expect, the problem is most likely due to some distortion of the guide arms on the camera front cover. In effect, the arms are holding the lens standard back further into the body than it should do, pushing the lens standard right back against the cocking rack. This creates an extra load on the cocking components, and typically the teeth at the top of the rack fail.
Analysis of bad racks that have been replaced in the course of repairs
- Total number of racks in survey 35 (100%)
- Racks with damage to upper teeth 28 (80%)
- Racks with damage to lower teeth 22 (57%)
Thirteen racks, or 37% of the sample show tooth damage at both ends.
Six racks show obvious signs of various desperate attempts to repair damage, or alter the rack to improve the mesh of the teeth, only one of these attempts looks likely to have been successful to any degree.
Of the twenty-eight racks with damage to upper teeth, twenty had stripped teeth, and the camera could not possibly have been working, eight have distorted teeth and it is possible that the camera still worked after a fashion, but the action of the film advance lever would probably have been noticeably rough.
Of the twenty-two racks with damage to the lower teeth, fourteen have stripped teeth and the camera could not have been working, the remaining eight show some distortion of the teeth, and possibly the camera still functioned, but with a rough feel to the film advance action.
So in total, twenty-seven of the racks were completely useless, eight probably would have worked, but not smoothly, and they probably would not have worked for much longer.